News
Recent news articles
Bending and breaking protoplanetary discs around a binary star
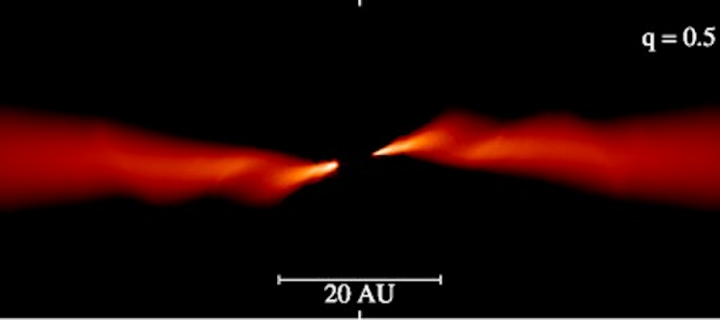
The environment in which stars and planets form is highly dynamic. Stars commonly form in binary or multiple systems within a vast cloud of molecular gas. Stellar systems are always on the move due to the initial turbulence and rotation of the gas that they formed from. Most young stars host protoplanetary discs, made up of gas and dust and from which planets form.
Confronting compositional confusion through characterising a sub-Neptune exoplanet
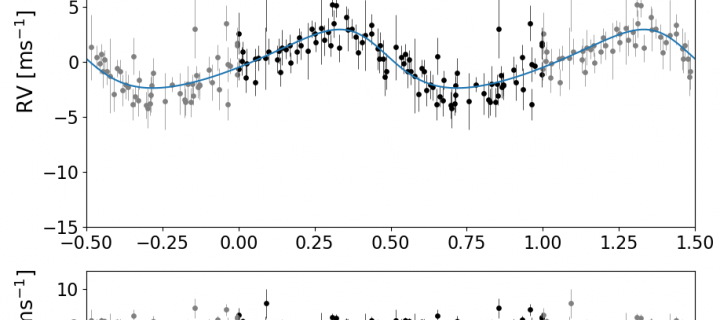
Precisely characterising exoplanet masses and radii can help to resolve a compositional confusion for small exoplanets and improve our understanding of the origin of these exoplanets and their evolution.
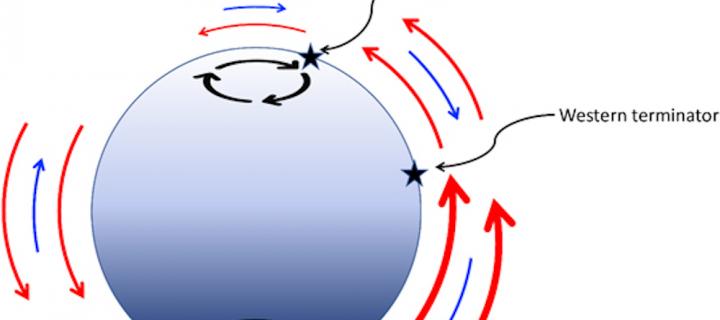
Weather patterns on Earth-like exoplanets could affect observations

Most potentially habitable rocky planets are expected to be in tidally locked orbits around small, cool stars. Just as the Moon always shows the same face to the Earth, these planets always have the same hemisphere facing their star.
Lightning-induced chemistry on tidally-locked, Earth-like exoplanets
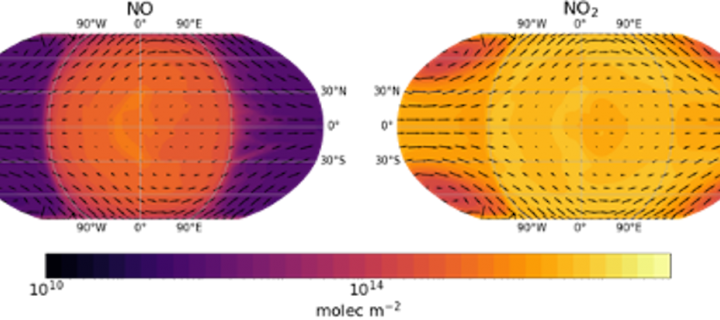
Using a 3-D coupled climate-chemistry model (CCM), we investigate the emergence of lightning and its chemical impact on the atmospheres of tidally-locked Earth-like exoplanets (nominally Proxima Centauri b). In a tidally-locked orbit, one side of the planet faces the star at all times, leading to dayside-nightside distinctions in the planetary environment.
Stratospheric wind and water vapour fluctuations on tidally locked exoplanets
Wind currents in the Earth’s equatorial stratosphere change direction every 26-28 months. Abundances of ozone, methane, water vapour, and other trace atmospheric gasses oscillate on the same timescale. This phenomenon is known as the “quasi-biennial oscillation” (QBO) and also occurs on other solar system planets (Jupiter and Saturn), though with different periods.
Chromium hydride in the atmosphere of hot Jupiter WASP-31b

First evidence for the presence of chromium hydride (CrH) in the atmosphere of a hot Jupiter, or a Jupiter-size planet orbiting close to its host star.
Fragmentation favoured in discs around higher mass stars

In work led by James Cadman, we investigate how a protoplanetary disc’s susceptibility to gravitational instability and fragmentation depends on the mass of its host star, finding that discs become increasingly prone to the effects of self-gravity with increasing stellar mass.
Ozone chemistry on tidally locked M dwarf planets
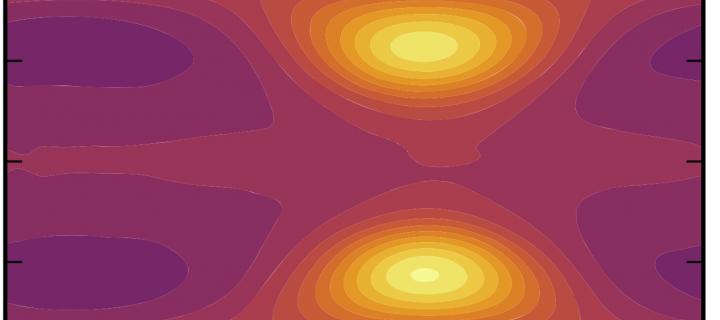
We explore atmospheric ozone dynamics on a tidally-locked M dwarf planet, nominally Proxima Centauri b, irradiated by a quiescent version of its host star.
2I/Borisov: A C2 depleted interstellar comet

Comet C/2019 Q4 (Borisov) was discovered on 30 August 2019 while cruising on an orbit with an eccentricity in excess of three. It is of unambiguous interstellar origin and was officially renamed 2I/Borisov on 24 September 2019.
Characterising long-period exoplanets

In this work we've been able to characterise the intermediate-mass long-period exoplanets in the PH-2 and Kepler-103 systems.
Iron-rich planet formed after distant worlds’ high-speed collision
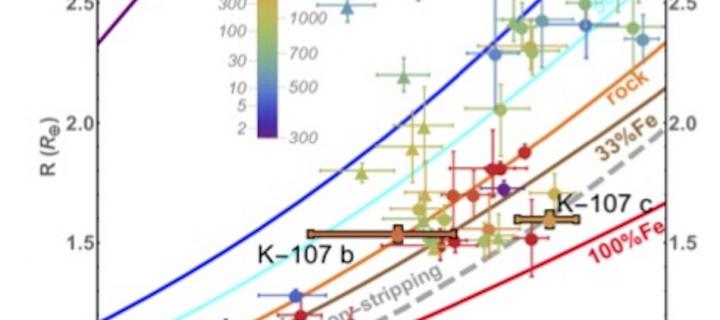
For the first time, evidence of an impact taking place between planets outside our Solar System has been found.
The three super-Earths around GJ 9827
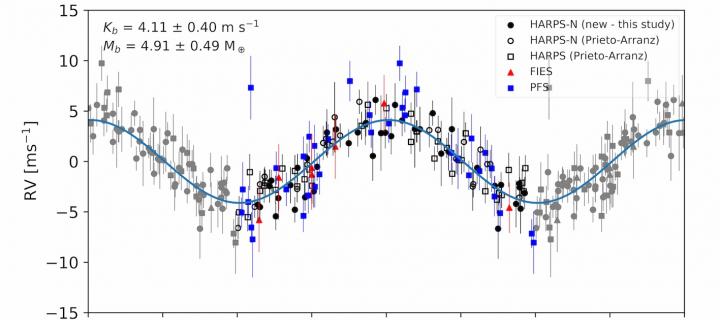
We use precise radial velocity measurements to estimate the masses of the super-Earths around GJ 9827. We find that two of these bracket the super-Earth radius gap and indicate that irradiation from the central star may have influenced the evolution of the inner planets in this system.
Estimating eta-Earth

Understanding the origin of very close-in, rocky exoplanets can help us to constrain the frequency of Earth-like exoplanets on orbits where liquid water may exist on their surface.
Observing the earliest stages of star and planet formation

Spiral waves detected in a disc around a very young star may be indicative of a gravitational instability.
Monitoring Weather Patterns with the Spitzer Space Telescope

In a recent paper we searched for evidence of weather patterns in the atmospheres of three free-floating ‘exoplanet analogues’ using the Spitzer Space Telescope.
Sculpting the population of planets formed via disc fragmentation
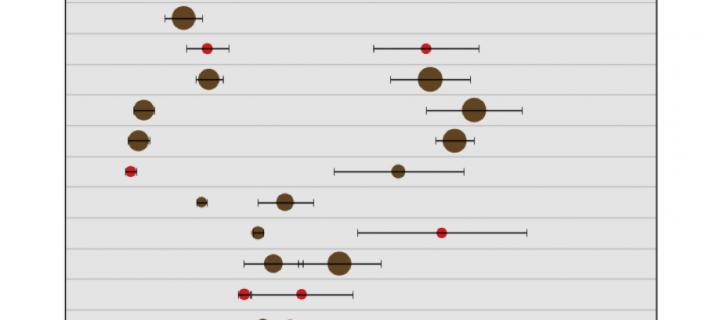
Fragment-fragment interactions can play a key role in sculpting the population of planets formed via direct collapse in gravitationally unstable protostellar discs
The Viewing Geometry of Brown Dwarfs Influences Their Spectral Appearance

Researchers at the Centre for Exoplanet Science investigated the effects of viewing geometry on the observed properties of brown dwarfs.
The properties of planets that form via disc instability

Investigating the properties of giant planets that form via direct gravitational collapse.
The formation of planets on wide orbits

Comparing observed exoplanet populations with synthetic populations so as to determine the likely formation mechanism of the known exoplanets.
Far-off planetary worlds may sustain life
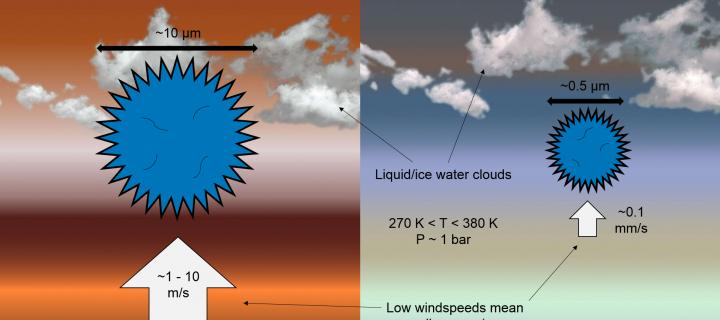
Life could exist in the atmospheres of brown dwarfs and gas giants, research suggests.

